Well, I’ll tell you what: It’s like we’ve been hit by a tidal wave of CBD, hasn’t it?
Everywhere you look, there it is.
Iced lattes, bath soaps, you name it – if it’s consumable or applicable, someone’s probably slapped some CBD in it.
It wasn’t always that way.
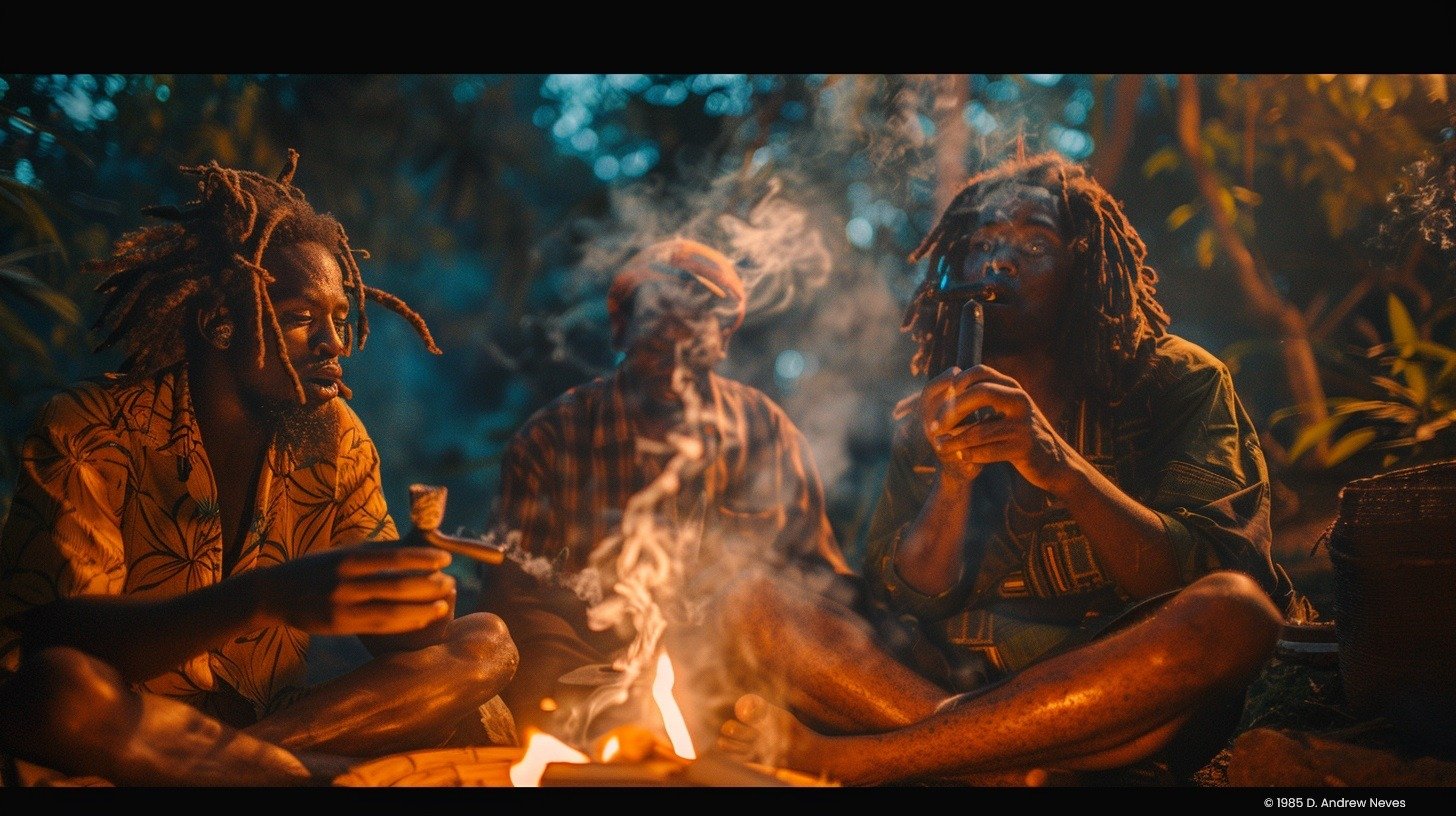
I still remember one of my trips to the Wareika Hills of Jamaica. It was a late spring evening, unusually chilly for a tropical island, as we climbed the rocky slopes, avoiding sharp rocks and thorn-bearing wild bushes. The climb was winding and tiring.
When I finally reached the encampment, Rastafarian “brethren,” some wearing locks, sat around a campfire smoking a “chillum pipe.” Others slapped the akete drums with slow, steady, and pulsating beats that felt like my body shaking.
The thick cloud of “Sinsemillia” smoke made me even more thirsty than high . . .
That was more than thirty years ago.
Today, all the rage is CBD, cannabidiol, one of the other chemicals in Cannabis sativa L. (marijuana) that does not produce the “high” associated with its use.
Key Takeaways
- Hemp microgreens are emerging as a nutritional powerhouse, offering a wealth of nutrients without the psychoactive effects associated with mature marijuana plants. They’re gaining attention for potential health benefits, culinary uses, and sustainable cultivation.
- Hemp microgreens contain a perfectly balanced ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids (3:1 to 4:1), all 9 essential amino acids, and are rich in vitamins E, C, and K. They’re also a significant source of minerals like potassium, calcium, iron, and zinc.
- These microgreens are packed with beneficial compounds, including CBD, which may help reduce anxiety and inflammation, as well as other cannabinoids like CBG and CBC, which have potential therapeutic properties. THC levels are kept very low (below 0.3%), making them non-psychoactive.
- Growing hemp microgreens is relatively easy and quick, with harvest 8-10 days after seeding. However, it’s crucial to select seeds that comply with legal THC limits and to stay informed about local regulations.
- Hemp microgreens offer a unique nutty and slightly peppery flavor profile, making them versatile for culinary applications in salads, smoothies, garnishes, and various dishes. They pair well with citrus fruits, avocados, nutty cheeses, and roasted vegetables.
MICROGREENS WEEKLY DIGEST
Unearth nature’s nutrient powerhouses.
Subscribe to receive:
- Expert tips to grow nutrient-packed microgreens
- Creative recipes to enjoy your homegrown harvest
- Latest science, industry insights, and market trends
Join our community of growers and health enthusiasts.
Cultivate your knowledge. Nourish your body.
Sign up now. Let’s grow together.
Hemp Microgreens: Controversial Plant to Superfood
The allure of the forbidden
Hemp microgreens: A nutritional powerhouse in disguise
Demystifying Cannabis sativa L.
Hemp vs. Marijuana: Clearing the Smoke
The Legal Landscape: Walking the Fine Line
Key points to consider:
The Nutritional Gold Mine
Essential fatty acids: Omega-3 and Omega-6 in perfect harmony
Complete protein profile: All 9 essential amino acids
Vitamins: A micronutrient bonanza
A Rich Mineral Profile
Antioxidants: Fighting free radicals with every bite
Health Benefits and Potential Risks
Anti-inflammatory properties
Stress and anxiety reduction
Heart Health Support
Skin Health
Considerations for drug testing and medication interactions
Cannabinoids in Hemp Microgreens
CBD: The calming compound
THC: Trace amounts and legal limits
Other beneficial phytocannabinoids: CBG, CBC, and more
Growing Hemp Microgreens
Most Researched Hemp Cultivars in the US, Canada, and the EU
Seed selection: Navigating legal waters
Cultivation techniques: From soil to harvest
Potential challenges and how to overcome them
The Future of Hemp Microgreens
Research frontiers: Unlocking more potential
Market trends: Growing demand and acceptance
Sustainability angle: Hemp as an eco-friendly crop
Culinary Applications
Flavor profile: Nutty, earthy, and versatile
Recipe ideas: Salads, smoothies, and beyond
Pairing suggestions: Complementary flavors and textures
Related Questions
How do hemp microgreens compare nutritionally to other popular microgreens like broccoli or kale?
Are there any potential side effects or risks associated with consuming hemp microgreens regularly?
How does the environmental impact of growing hemp microgreens compare to growing other crops?
Are there any regulations or certifications specific to hemp microgreens that consumers should look for when purchasing?
Wrap-up The Forbidden Microgreen
Embracing the forbidden: Hemp microgreens as a nutritional ally
Call to action: Exploring hemp microgreens responsibly
It’s become the darling of the wellness world faster than you can say “chakra realignment.”
But let’s not kid ourselves – this isn’t exactly breaking news to the cannabis crowd.
They’ve been singing CBD’s praises from the rooftops for donkey’s years, haven’t they?
All starry-eyed about its supposed health benefits and natural healing properties.
And now, well, it’s like the rest of us have finally caught up.
We’re all suddenly enthralled by the idea of hemp-based products as some sort of holistic wonder cure.
A more ‘natural’ alternative to those pesky pharmaceuticals, eh?
It’s funny, isn’t it?
How something can go from being the domain of a few enthusiasts to the must-have ingredient in every wellness guru’s toolkit practically overnight.
One minute, it’s niche; the next, it’s mainstream.
That’s progress for you, I suppose. Or clever marketing. Or both. Who can tell these days?
The allure of the forbidden
Hemp, Cannabis sativa L., has long been a subject of fascination, controversy, and intense debate.
Its complex history, nuanced chemistry, and multifaceted potential uses have driven curiosity and sparked discussions across various fields, from medicine to agriculture.
The blurred lines between hemp and marijuana, along with the presence of compounds like ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and CBD, add layers of intrigue to this already captivating plant.
Hemp microgreens: A nutritional powerhouse in disguise
Amidst the controversy surrounding Cannabis sativa L., a lesser-known but influential byproduct has emerged: hemp microgreens.
These young, leafy greens are harvested just after the first true leaves appear, offering a wealth of nutrients without the psychoactive effects associated with mature marijuana plants.
Hemp microgreens are gaining attention for their potential health benefits, culinary uses, and sustainable cultivation practices.
Hemp vs. Marijuana: Clearing the Smoke
Here’s the thing: If you want to really get a handle on Cannabis sativa L., you’ve got to wrap your head around the key differences between hemp and marijuana.
They may come from the same plant family, but make no mistake – these two cousins are worlds apart when it comes to their uses and legal status.
Knowing how to tell hemp from marijuana isn’t just botanical trivia. It’s essential knowledge for anyone looking to navigate the complex landscape of cannabis products and regulations.
| Hemp | Cannabis sativa L. is primarily cultivated for industrial and therapeutic benefits and contains less than 0.3% THC by dry weight. It’s used for producing textiles, bioplastics, construction materials, and CBD products. |
| Marijuana | Cannabis sativa or Cannabis indica species are grown for their psychoactive effects and contain higher levels of THC, typically above 0.3%. It’s used for recreational and medicinal purposes. |
The Legal Landscape: Walking the Fine Line
The legal status of Cannabis sativa L. products varies widely across different jurisdictions. In many countries, hemp and hemp-derived products (including microgreens) are legal if they contain less than 0.3% THC. However, marijuana remains illegal or heavily regulated in many parts of the world.
This table provides a clear comparison of the legal status of hemp and marijuana across different countries and regions.
| Country | Hemp | Marijuana |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Legal nationwide since the 2018 Farm Bill, hemp-derived products containing less than 0.3% THC | Legal for recreational use in several states, legal for medical use in many others, and federally illegal |
| India | Legal in some states like Uttarakhand, with strict regulations on THC content | Illegal for recreational use; used traditionally; can be prescribed for medical use. |
| United Kingdom | Legal for cultivation with a license; production of hemp flowers and leaves tightly controlled | Illegal for recreational use; medicinal use is legal but tightly regulated and available under prescription |
| Australia | Legal for industrial purposes; food products made from hemp are legal | Illegal for recreational use; medicinal cannabis is legal and can be prescribed under certain conditions |
| Canada | Legal for cultivation and industrial use; hemp-derived CBD products are legal | Fully legal for both recreational and medicinal use since October 2018 |
| Europe (varies) | Many countries have legalized hemp with low THC content | Laws vary by country; some allow medical use, others legalize recreational use (e.g., Netherlands, Portugal) |
| South America | Varies by country; Uruguay has fully legalized cannabis; others allow for medical use. | Varies by country; Uruguay has fully legalized cannabis; others allow for medical use. |
| Asia (varies) | Generally illegal in most countries | Generally illegal in most countries; some exceptions for medical use (e.g., Thailand) |
| Africa (varies) | Legal status varies | Legal status varies; South Africa allows personal use; some countries exploring medical cannabis regulations. |
Key points to consider:
- Regulations often focus on THC content to distinguish between legal hemp and controlled marijuana.
- Some areas allow medical use of marijuana with proper licensing.
- Local ordinances may impose additional restrictions, even in areas where cannabis is broadly legal.
- NOTE: Always consult local laws and regulations before cultivating or using any Cannabis sativa L. products.
The hemp food industry is expanding, and with it, the need to know what exactly is in these hemp products and, more specifically, what their phytocannabinoid profile is.
Yes, this food is high in good stuff like polyphenols and flavonoids, so it’s a promising and thriving market. But there really isn’t that much literature out there, and what’s there is very conflicted about the nature of phytocannabinoids.
Nutritional Analysis
| Name | Amount | % RDI |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 4.68 g | 0.0013197969543147 |
| Energy | 586 kcal | |
| Protein | 31.56 g | 0.46411764705882 |
| Total lipid (fat) | 48.75 g | 0.78629032258065 |
| Ash | 6.38 g | |
| Carbohydrate, by difference | 8.67 g | 0.02752380952381 |
| Fiber, total dietary | 4.0 g | 0.10526315789474 |
| Sugars, total including NLEA | 1.5 g | 0.03 |
| Calcium, Ca | 70 mg | 5.40% |
| Iron, Fe | 7.95 mg | 44.20% |
| Magnesium, Mg | 700 mg | 167.00% |
| Phosphorus, P | 1650 mg | 236.00% |
| Potassium, K | 1200 mg | 25.50% |
| Zinc, Zn | 9.9 mg | 90.00% |
| Copper, Cu | 1.6 mg | 178.00% |
| Manganese, Mn | 7.6 mg | 330.00% |
| Vitamin C, total ascorbic acid | 0.4 mg | 33.00% |
| Thiamin | 0.4 mg | 33.00% |
| Riboflavin | 0.12 mg | 9.20% |
| Niacin | 2.43 mg | 15.00% |
| Pantothenic acid | 1.36 mg | 27.00% |
| Vitamin B-6 | 0.12 mg | 2.40% |
| Folate, total | 110 µg | 28.00% |
| Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) | 0.80 mg | 5.00% |
| Vitamin K (phylloquinone) | 15 µg | 12.50% |
| Fatty acids, total saturated | 4.600 g | |
| Fatty acids, total monounsaturated | 5.400 g | |
| Fatty acids, total polyunsaturated | 38.100 g | |
| Tryptophan | 0.393 g | |
| Threonine | 1.223 g | |
| Isoleucine | 1.506 g | |
| Leucine | 2.424 g | |
| Lysine | 0.9 g | |
| Methionine | 0.942 g | |
| Cystine | 0.759 g | |
| Phenylalanine | 1.307 g | |
| Tyrosine | 1.293 g | |
| Valine | 2.139 g | |
| Arginine | 4.550 g | |
| Histidine | 0.904 g | |
| Alanine | 1.251 g | |
| Aspartic acid | 3.527 g | |
| Glutamic acid | 7.376 g | |
| Glycine | 1.191 g | |
| Proline | 1.443 g | |
| Serine | 1.561 g |
Essential fatty acids: Omega-3 and Omega-6 in perfect harmony
Hemp microgreens offer a perfectly balanced ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids, typically ranging from 3:1 to 4:1. This balance is crucial for promoting heart health, reducing inflammation, and supporting overall well-being.
Explore more hemp-based products at this hemp store for comprehensive nutritional options.
Complete protein profile: All 9 essential amino acids
Hemp microgreens stand out in the plant protein world. Unlike most veggie options, they deliver all nine essential amino acids your body can’t make. That’s the complete protein package, right there in those tiny leaves.
Hemp protein boasts all 20 amino acids, including the 10 essential ones our bodies can’t make. This full spectrum, in the right amounts, makes hemp protein a standout complete protein source for optimal health.
Hemp seed contains up to 36% protein. The protein in hemp is comprised of approximately 65% edestin. It is considered to be similar to the protein found in human blood plasma and is easily absorbed by the body.
No other single food source, with the exception of soy, has the essential amino acids in such an easily digestible form, nor does it have the essential fatty acids in a perfect ratio to meet human nutritional needs.
For those following plant-based diets, hemp microgreens offer a protein-rich option that compares favorably to animal-derived proteins in terms of nutritional value. Their unique composition makes them a standout choice for vegetarians and vegans seeking high-quality protein sources.
Vitamins: A micronutrient bonanza
Hemp microgreens are rich in various vitamins and minerals, including:
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin K
A Rich Mineral Profile
The diverse mineral nutrient profile of hemp microgreens supports overall health and wellness, from boosting immune function to promoting bone health.
The research by Corrado et al., 2022 emphasizes the potential of hemp microgreens to address mineral malnutrition while supporting agricultural sustainability.
Hemp microgreens are, above all, a good source of potassium, calcium, and manganese among macroelements and iron and zinc among microelements. Moreover, hemp can be considered a sustainable microgreen to meet the nutrient requirement of selenium.
The following table summarizes the mineral composition of hemp microgreens based on recent research findings[1]:
| Mineral nutrients | Estimated Daily Intake (EDI) | Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) % | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macronutrients (mg-1/day) | ||||
| Phosphorus (P) | 8.21 | 0.82 | Lower abundance compared to K. | |
| Potassium (K) | 49.96 | 1.4 | Highest concentration among macroelements. | |
| Calcium (Ca) | 25.05 | 2.85 | Significant source, contributing to dietary calcium intake. | |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 15.18 | 4.38 | Present in lower amounts compared to K and Ca. | |
| Micronutrients (μg-1/day) | ||||
| Iron (Fe) | 326.58 | 2.18 | Notable for human dietary needs, high bioavailability. | |
| Copper (Cu) | 46.91 | 2.35 | Commonly found in microgreens, specific data is not provided. | |
| Zinc (Zn) | 234.32 | 1.56 | A higher concentration than in adult hemp is essential for health. | |
| Selenium (Se) | 18.73 | 33.91 | ||
| Boron (B) | 25.02 | 0.83 | ||
| Chromium (Co) | 1.35 | 1.13 | Low accumulators across varieties. | |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 6.64 | 8.85 | ||
| Manganese (Mn) | 221.53 | 4.43 | ||
Hemp microgreens exhibit a rich mineral profile, providing significant contributions to essential nutrients such as potassium, calcium, and iron. Additionally, they show a lower tendency to accumulate harmful heavy metals, making them a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Antioxidants: Fighting free radicals with every bite
Hemp microgreens are rich in antioxidants, which serve as a defense against cellular damage inflicted by free radicals. This protective effect could potentially lower the likelihood of developing long-term health issues, including cardiovascular disease and certain cancers.
[1] To understand how hemp microgreens nourish the body, the researchers calculated two key measures: First, the EDI – that’s how many milligrams of each mineral a person typically consumes daily from hemp microgreens. They based this on the average portion size of about 3 tablespoons. Second, the RDA – the percentage of your daily mineral needs met by that serving. They compared the mineral content to recommended daily intakes established by nutrition experts. For example, they suggest 1000 mg of bone-building calcium and 15 mg of energizing iron each day.
Hemp microgreens burst with zesty malic and citric acids alongside a bouquet of beneficial compounds (Pannico et al., 2022). They pack a nutritional punch, brimming with non-intoxicating cannabinoids and soothing flavonoids.
Anti-inflammatory properties
The cannabinoids and omega-3 fatty acids in hemp microgreens may help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially benefiting conditions such as:
- Arthritis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Cardiovascular disease
Stress and anxiety reduction
CBD and other substances found in hemp microgreens might help reduce stress and anxiety by working with the body’s endocannabinoid system.
Heart Health Support
The balanced fatty acid profile and antioxidants in hemp microgreens may contribute to heart health by:
- Reducing inflammation
- Lowering blood pressure
- Improving cholesterol levels
Skin Health
Hemp bursts with skin-nourishing goodness.
Its omega-rich oils (omega-3 and omega-6) plump and soften, while amino acids boost collagen production, leaving your skin dewy and smooth.
This natural powerhouse helps ward off wrinkles, giving you a radiant, youthful glow from the inside out.
Considerations for drug testing and medication interactions
While hemp microgreens contain only trace amounts of THC, regular consumption could potentially lead to false positives on drug tests.
Furthermore, cannabinoids might interact with specific medications, especially those that are broken down by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system.
NOTE: Before adding hemp microgreens to your diet, it’s essential to seek advice from a medical expert, particularly if you’re taking any medications or could be subject to drug testing.
One recently published study (Ferri et al., 2024) unveiled a unique fingerprint of cannabis compounds in various hemp types. Unexpectedly, even “low-content” hemp varieties packed a punch, brimming with these aromatic and potentially beneficial phytocannabinoids, challenging our assumptions about their chemical makeup.
CBD: The calming compound
Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive substance present in hemp microgreens, has become popular due to its possible health benefits, including:
- Anxiety and stress relief
- Pain management
- Reduction of inflammation
- Improved sleep quality
Looking for premium hemp products? Visit our recommended hemp store.
THC: Trace amounts and legal limits
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary substance in marijuana that causes people to feel high. In hemp microgreens, THC levels are kept very low, below 0.3%, which is the legal limit. This small amount isn’t enough to make you feel high.
However, it may contribute to the overall beneficial properties of the plant through the “entourage effect.”[2]
Other beneficial phytocannabinoids: CBG, CBC, and more
In the same study (Ferri et al., 2024), hemp microgreens burst with CBCA (cannabidiolic acid), a tangy compound dominating up to 63.2% of their phytocannabinoid. The zesty Eletta Campana variety packed a whopping 19.34 mg/100 g of CBDA. CBCA levels skyrocketed from seed to sprout, hinting at its crucial role in early growth.
Hemp microgreens contain a variety of other cannabinoids, each with potential therapeutic properties:
- Cannabigerol (CBG): Known as the “mother cannabinoid,” CBG is a precursor to other cannabinoids and may have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties.
- Cannabichromene (CBC): This non-psychoactive compound has shown promise in pain relief and mood regulation.
- Cannabinol (CBN): Often associated with improved sleep quality and pain relief.
[2] The entourage effect is the idea that all the different compounds in cannabis (like THC, CBD, and various terpenes) work better together than they do alone. This means that the combination of these substances can produce a stronger or more balanced effect in the body than any single one of them by itself.
Unlike their mature counterparts, there is no specific time of the year for microgreens growth, and the only requirement for their production is the availability of good certified seeds with high germinability.
Most Researched Hemp Cultivars in the US, Canada, and the EU
| Cultivar | Notable Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Antal | High levels of certain phytocannabinoids and amino acids |
| Asso | High seed yield; suitable for food and oil production |
| Beniko | High fiber content; suitable for textile production |
| Bialobrzeskie | Known for its high fiber yield and quality, it is widely grown in Europe. |
| Carmagnola | Traditional Italian variety; high fiber content |
| Carmaleonte | High CBD content; low THC |
| Fedora 17 | High CBD content; used extensively for CBD oil production |
| Felina 32 | Rich in fiber; used for both fiber and seed production |
| Finola | Highest concentration of cannflavins and total polyphenols; lowest levels of Δ9-THC |
| Futura 75 | High yield; well-adapted to European climates |
| Glecia | Balanced cannabinoid profile; moderate levels of CBD and CBG |
| Kompolti | Highest fresh yield; significant concentrations of bioactive compounds |
| Lovrin 110 | High seed yield; good for oil production |
| Monoica | High seed and fiber yield; suitable for dual-purpose cultivation |
| Santhica 70 | THC-free variety; high in CBD and other cannabinoids |
| Santika | Balanced profile of cannabinoids; moderate CBD and THC content |
| Silvana | Boasting superior levels of both total and essential amino acids, contain significant amounts of cannflavins A and B. Additionally, they feature moderate concentrations of the cannabinoids CBD and CBG. |
| Tiborszallasi | High biomass yield; good adaptability to various climates |
| Tisza | Considerable levels of phytocannabinoids and amino acids contribute to overall yield and nutritional profile. |
| Uso31 | Less prominent in bioactive compound concentrations; lowest nutritional value among studied cultivars |
This table provides an overview of some of the most researched hemp cultivars, highlighting their notable characteristics and uses.
Seed selection: Navigating legal waters
When growing hemp microgreens, it’s crucial to select seeds that comply with legal THC limits. Key considerations include:
- Choose certified seeds from approved suppliers
- It’s imperative to work with a seed company that provides feminized seeds
- Verify that the seeds are from hemp varieties with THC levels below 0.3%
- Keep documentation of seed sourcing for regulatory compliance
Cultivation techniques: From soil to harvest
Growing hemp microgreens can be done using soil or hydroponic systems. Hemp has a speedy growth rate, with the first pair of true leaves forming typically 8-10 days after seeding (Pannico et al., 2022).
Here are some critical steps:
- Prepare growing trays with well-draining soil or growing medium
- Sow seeds densely and cover lightly with soil
- Maintain proper temperature (65-75°F) and humidity (50-60%)
- Provide adequate light (14-16 hours per day)
- Water regularly, keeping the soil moist but not waterlogged
- Harvest when the first leaf pairs form, typically 8-10 days after seeding
Potential challenges and how to overcome them
Common challenges in growing hemp microgreens include:
- Mold and fungal growth: Ensure proper air circulation and avoid overwatering
- Uneven germination: Use high-quality seeds and maintain consistent moisture levels
- Legality concerns: Stay informed about local regulations and maintain proper documentation
- Pest management: Implement organic pest control methods to protect your crop
Research frontiers: Unlocking more potential
Ongoing research is exploring:
- Optimization of growing conditions to enhance nutrient profiles
- Potential medicinal applications of hemp microgreen extracts
- Development of new hemp varieties specifically for microgreen production
Market trends: Growing demand and acceptance
The market for hemp microgreens is expanding, driven by:
- Increasing consumer awareness of their health benefits
- Growing demand for plant-based protein sources
- Shift towards sustainable and locally-grown food options
Sustainability angle: Hemp as an eco-friendly crop
Hemp micro greens offer several environmental benefits:
- Rapid growth cycle, requiring minimal resources
- Potential for vertical farming and urban agriculture
- Natural pest resistance, reducing the need for pesticides
- Soil remediation properties, improving soil health
According to one study (Corado et al., 2022), each variety of hemp microgreens offers a unique flavor profile, promising exciting possibilities for health-conscious cuisine.
With minimal oxalic acid, these microgreens are gentle on the palate and body, outshining many of their leafy competitors in both taste and wellness potential.
Flavor profile: Nutty, earthy, and versatile
Hemp micro greens offer a unique flavor profile that can enhance various dishes:
- Nutty undertones reminiscent of sunflower seeds
- Subtle earthy notes that complement savory dishes
- A slight pepperiness that adds depth to salads and sandwiches
Recipe ideas: Salads, smoothies, and beyond
Incorporate hemp microgreens into your diet with these ideas:
- Add to mixed green salads for extra nutrition and flavor
- Blend into smoothies for a nutrient boost
- Use as a garnish for soups, stews, and grain bowls
- Incorporate into pesto or other herb-based sauces
- Top avocado toast or sandwiches for added crunch and nutrition
Pairing suggestions: Complementary flavors and textures
Hemp microgreens pair well with:
- Citrus fruits like lemon and orange
- Creamy avocado
- Nutty cheeses like goat cheese or feta
- Roasted vegetables
- Grilled meats or plant-based proteins
How do hemp microgreens compare nutritionally to other popular microgreens like broccoli or kale?
Research suggests hemp microgreens are exceptionally high in protein and essential fatty acids compared to other microgreens. For example, hemp microgreens contain all 9 essential amino acids, while many other microgreens lack one or more. They also have an ideal 3:1 to 4:1 ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids, which is rare among plant sources.
Are there any potential side effects or risks associated with consuming hemp microgreens regularly?
Generally, hemp microgreens are considered safe for most people, but some individuals may experience mild digestive issues or allergic reactions. It’s always best to start with small amounts and consult a healthcare provider, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
How does the environmental impact of growing hemp microgreens compare to growing other crops?
Hemp is generally considered more environmentally friendly than many crops due to its rapid growth, low water requirements, and natural pest resistance. One study found that hemp requires about half the land and water to produce the same amount of protein compared to soybeans.
Are there any regulations or certifications specific to hemp microgreens that consumers should look for when purchasing?
Currently, there’s no standardized certification specifically for hemp microgreens. However, consumers can look for organic certifications, which ensure the product is grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers. Additionally, reputable producers should be able to provide third-party lab testing results showing cannabinoid content and confirming THC levels are below the legal limit of 0.3%.
Embracing the forbidden: Hemp microgreens as a nutritional ally
Hemp microgreens represent a fascinating intersection of nutrition, culinary innovation, and sustainable agriculture. By understanding the complexities surrounding Cannabis sativa L. and its various forms, we can better appreciate the unique benefits of hemp microgreens.
Call to action: Exploring hemp microgreens responsibly
As you consider incorporating hemp microgreens into your diet or exploring their cultivation, remember to:
- Stay informed about local laws and regulations
- Source seeds and products from reputable suppliers
- Start small and experiment with different culinary applications
- NOTE: Consult with healthcare professionals if you have any health concerns
- Support research and sustainable practices in the hemp industry
By approaching hemp microgreens with knowledge and responsibility, we can unlock their full potential as a nutritious, versatile, and sustainable food source for the future.
MICROGREENS WEEKLY DIGEST
Unearth nature’s nutrient powerhouses.
Subscribe to receive:
- Expert tips to grow nutrient-packed microgreens
- Creative recipes to enjoy your homegrown harvest
- Latest science, industry insights, and market trends
Join our community of growers and health enthusiasts.
Cultivate your knowledge. Nourish your body.
Sign up now. Let’s grow together.
Research
Cerino, P., Buonerba, C., Cannazza, G., D’Auria, J., Ottoni, E., Fulgione, A., Di Stasio, A., Pierri, B., & Gallo, A. (2021). A Review of Hemp as Food and Nutritional Supplement. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, 6(1), 19–27. https://doi.org/10.1089/can.2020.0001
Corrado, G., Pannico, A., Zarrelli, A., Kyriacou, M. C., De Pascale, S., & Rouphael, Y. (2022). Macro and trace element mineral composition of six hemp varieties grown as microgreens. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 114, 104750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104750
Ferri, E., Russo, F., Maria Angela Vandelli, Paris, R., Laganà, A., Anna Laura Capriotti, Gallo, A., Siciliano, A., Carbone, L., Gigli, G., Citti, C., & Cannazza, G. (2024). Analysis of phytocannabinoids in hemp seeds, sprouts, and microgreens. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 116181–116181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116181
Kacper Piotr Kaminski, Hoeng, J., Goffman, F., Schlage, W. K., & Latino, D. (2024). Opportunities, Challenges, and Scientific Progress in Hemp Crops. Molecules/Molecules Online/Molecules Annual, 29(10), 2397–2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102397
Li, L., Yu, S., Chen, J., Cheng, C., Sun, J., Xu, Y., Deng, C., Dai, Z., Yang, Z., Chen, X., Tang, Q., Su, J., & Zhang, X. (2022). Releasing the Full Potential of Cannabis through Biotechnology. Agronomy, 12(10), 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102439
Pannico, A., Kyriacou, M. C., El-Nakhel, C., Graziani, G., Carillo, P., Corrado, G., Ritieni, A., Rouphael, Y., & De Pascale, S. (2022). Hemp microgreens as an innovative functional food: Variation in the organic acids, amino acids, polyphenols, and cannabinoids composition of six hemp cultivars. Food Research International, 161, 111863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111863
Pellati, F., Brighenti, V., Sperlea, J., Marchetti, L., Bertelli, D., & Benvenuti, S. (2018). New Methods for the Comprehensive Analysis of Bioactive Compounds in Cannabis sativa L. (hemp). Molecules, 23(10), 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102639
Zheljazkov, V. D., Sikora, V., Dincheva, I., Kačániová, M., Astatkie, T., Semerdjieva, I. B., & Latkovic, D. (2020). Industrial, CBD, and Wild Hemp: How Different Are Their Essential Oil Profile and Antimicrobial Activity? Molecules, 25(20), 4631. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204631