Back in the ‘60s, when I was running around on my family’s farm, few people thought about watercress microgreens nutrition. A generation raised on TV dinners and canned vegetables, blissfully unaware of the nutritional powerhouses growing quietly in nature’s corners.
Fast forward to today, and I find myself marveling at these tiny green wonders. Watercress microgreens, barely larger than the period at the end of this sentence, pack a punch that would make my childhood broccoli blush. They’re bursting with vitamins A, C, and K – an alphabet soup of nutrients that would have boggled the minds of the food scientists who crafted those TV dinners of my youth.
As I tend to my own garden, I can’t help but reflect on how our understanding of nutrition has evolved. These microgreens, with their calcium and manganese content, represent a return to the basics – the kind of wholesome nutrition my grandparents might have known before the age of processed foods took hold.
I think about the bioactive compounds in these little leaves – chlorophyll, glucosinolates, polyphenols. Terms that would have sounded like science fiction in my childhood now roll off the tongue of health-conscious individuals at the farmer’s market.
Adding a handful to my salad, I’m struck by how something so small can make such a big difference. It’s a reminder that, in nature, great things often come in small packages.
As I crunch on these nutrient-dense microgreens, I can’t help but wonder: what other hidden treasures of nutrition are we yet to discover?
Key Takeaways
- Watercress microgreens are rich in vitamins A, B complex, C, E, and K.
- You can find essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium in them.
- Nearly 89% of watercress microgreens are water, providing essential hydration.
- They are packed with bioactive compounds like glucosinolates and isothiocyanates.
- Watercress microgreens offer enhanced antioxidant levels compared to mature watercress.
INTERESTED IN MICROGREENS?
Join the community
Join more than 100,000 other health-conscious individuals and couples who visit our site and receive weekly emails from us to help them grow more microgreens to live healthier and longer lives.
Watercress Microgreen: A Nutritional Powerhouse
Brief overview of watercress (Nasturtium officinale)
Growing popularity of watercress microgreens
Botanical Characteristics of Watercress
Traditional uses
Nutritional Profile of Watercress Microgreens
Macronutrients
Micronutrients
Phytochemicals
Essential Oil Composition
Health Benefits of Watercress Microgreens
Anticancer properties
Anti-inflammatory effects
Cardiovascular health
Liver protection
Other potential benefits
Watercress Microgreens: Comparison with Mature Watercress
Nutritional differences
Phytochemical profile variations
Advantages of microgreens
Watercress Microgreens: Culinary Applications
Flavor profile
Incorporation into dishes
Pairing suggestions
Other Applications
Cultivation of Watercress Microgreens
Optimal growing conditions
Light requirements
Harvesting time
Optimization of cultivation techniques
Enhancement of bioactive compounds
Clinical studies on health benefits
How Do Watercress Microgreens Differ From Other Microgreens Nutritionally?
Can Watercress Microgreens Help With Weight Management?
Are There Any Potential Allergies Associated With Consuming Watercress Microgreens?
What Are the Best Storage Methods for Watercress Microgreens?
How Does Light Exposure Affect the Nutrient Content of Watercress Microgreens?
Wrap-up: Watercress Microgreens Nutrition

Picture this: a carpet of emerald-green leaves kissed by morning dew. That’s watercress, a perennial herb packed with flavor and nutrients. But have you heard about watercress microgreens? They’re not just a culinary delight—they’re a health superstar.
Brief overview of watercress (Nasturtium officinale)
Watercress, or Nasturtium officinale, is a member of the Brassicaceae family. It thrives in aquatic environments and boasts impressive medicinal properties. But here’s the kicker: watercress microgreens pack all these benefits into tiny, nutrient-dense shoots.
Growing popularity of watercress microgreens
Why the sudden buzz? Well, watercress microgreens offer a concentrated dose of nutrition in a small package. They’re easy to grow at home and add a peppery kick to any dish. Want to try them? Look for seeds in bulk on Amazon, or find them on sale at your local market.
Botanical Characteristics of Watercress
Imagine delicate stems reaching up to 60 cm, adorned with dark green leaves and white flowers. That’s mature watercress. Now, shrink that down to tender microgreens, and you’ve got a powerhouse of flavor and nutrients.
As part of the Brassicaceae family, watercress shares traits with mustard and cabbage. But here’s the exciting part: its microgreens offer unique benefits under specific growing conditions.
Traditional uses
For centuries, watercress has been used to treat various ailments. And guess what? Its microgreens carry on this legacy, offering traditional benefits in a modern, convenient form.
| Name | Amount | Unit | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 95.1 g | 3546 g | 2.68% |
| Energy | 11 kcal | ||
| Protein | 2.3 g | 68 g | 3.4% |
| Total lipid (fat) | 0.1 g | 62 g | 0.2% |
| Carbohydrate, by difference | 1.29 g | 315 g | 0.4% |
| Fiber, total dietary | 0.5 g | 38 g | 1.3% |
| Sugars, total including NLEA | 0.2 g | 50 g | 0.4% |
| Calcium, Ca | 120 mg | 1000 mg | 12.0% |
| Iron, Fe | 0.2 mg | 18 mg | 1.1% |
| Magnesium, Mg | 21 mg | 420 mg | 5.0% |
| Phosphorus, P | 60 mg | 0.7 g | 8.6% |
| Potassium, K | 330 mg | 3400 mg | 9.7% |
| Sodium, Na | 41 mg | 1500 mg | 2.7% |
| Zinc, Zn | 0.11 mg | 11 mg | 1.0% |
| Copper, Cu | 0.077 mg | 900 mcg | 7.8% |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.244 mg | 2.3 mg | 10.61% |
| Selenium, Se | 0.9 µg | 55 mcg | 1.6% |
| Vitamin C, total ascorbic acid | 43 mg | 90 mg | 47.8% |
| Thiamin | 0.09 mg | 1.2 mg | 7.5% |
| Riboflavin | 0.12 mg | 1.3 mg | 9.2% |
| Niacin | 0.2 mg | 16 mg | 1.3% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.31 mg | 5 mg | 6.20% |
| Vitamin B-6 | 0.129 mg | 1.3 mg | 9.9% |
| Folate, total | 9 µg | 400 mcg | 2.3% |
| Choline, total | 9 mg | 0.55 g | 1.6% |
| Vitamin A, RAE | 160 µg | 900 mcg | 17.8% |
| Carotene, beta | 1910 µg | 900 mcg | 212.2% |
| Lutein + zeaxanthin | 5770 µg | 6000 mcg | 96.2% |
| Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) | 1 mg | 15 mg | 6.7% |
| Vitamin K (phylloquinone) | 250 µg | 120 mcg | 208.3% |
| Fatty acids, total saturated | 0.027 g | ||
| Fatty acids, total monounsaturated | 0.008 g | ||
| Fatty acids, total polyunsaturated | 0.035 g | ||
| Tryptophan | 0.03 g | 1100 mg | 2.73% |
| Threonine | 0.133 g | 2400 mg | 5.54% |
| Isoleucine | 0.093 g | 2800 mg | 3.32% |
| Leucine | 0.166 g | 6600 mg | 2.52% |
| Lysine | 0.134 g | 5800 mg | 2.31% |
| Methionine | 0.02 g | 2500 mg | |
| Cystine | 0.007 g | 1.08% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.114 g | 6000 mg | |
| Tyrosine | 0.063 g | 2.95% | |
| Valine | 0.137 g | 3500 mg | 3.91% |
| Arginine | 0.15 g | ||
| Histidine | 0.04 g | 1900 mg | 2.11% |
| Alanine | 0.137 g | ||
| Aspartic acid | 0.187 g | ||
| Glutamic acid | 0.19 g | ||
| Glycine | 0.112 g | ||
| Proline | 0.096 g | ||
| Serine | 0.06 g |
Macronutrients
When you savor the crisp, peppery taste of watercress microgreens, you’re not just delighting your palate; you’re nourishing your body with a rich macronutrient profile.
Watercress microgreens, with their high water content of 88.94%, offer a hydrating burst of invigoration that enriches both their nutritional profile and culinary appeal.
Carbohydrates emerge as essential components, contributing both energy and essential sugars to support your body’s daily functions.
Micronutrients
When you investigate the nutritional profile of watercress microgreens, you’ll come across an impressive array of vitamins. Vitamins C and K are in abundance, and vitamins A, B complex, and E each contribute to their potent health benefits.
Exploring the mineral content of watercress microgreens uncovers a wealth of essential micronutrients, such as calcium, potassium, copper, phosphorus, and manganese.
Phytochemicals
These tiny greens are rich in vibrant orange and yellow carotenoids (beta carotene), polyphenols, anthocyanins, and potent glucosinolates, each contributing to their vibrant color and powerful health benefits.
Essential Oil Composition
When you examine the essential oil composition of watercress microgreens, you’ll find that powerful isothiocyanates, particularly benzyl isothiocyanate, dominate it.
This compound, along with others like benzylnitrile, not only gives watercress its unique aroma but also harbors potential health benefits, including anticancer and anti-inflammatory properties.
As you nurture others with these microgreens, you’re infusing their lives with nature’s potent, health-boosting essence.

Watercress microgreens: tiny green powerhouses packed with health benefits. But what makes them so special? Let’s dive in.
Anticancer properties
Did you know these vibrant greens could help guard against cancer? It’s true! They’re rich in isothiocyanates that fight breast cancer cells, reduce DNA damage, and boost your immune system. Imagine biting into nature’s own cancer-fighting pharmacy.
Anti-inflammatory effects
But that’s not all. These peppery leaves also combat inflammation. How? Through their natural compounds that soothe swelling and pain. Picture offering relief to a friend with just a handful of these microgreens.
Cardiovascular health
Now, let’s talk about heart health. These little greens are bursting with nutrients that support your ticker. They can help lower blood pressure, reduce arterial inflammation, and boost your heart’s vigor. Who knew such small leaves could pack such a punch?
Liver protection
But wait, there’s more! Watercress microgreens are also liver guardians. They work quietly within you, fighting oxidative stress and shielding your liver from harm. It’s like having a personal bodyguard for this vital organ.
Other potential benefits
And that’s just the beginning. These microgreens can enhance immunity, promote overall wellness, and make a big difference in your health journey. So why not give them a try? Your body will thank you.
I have become fascinated by the intricate world of plants. And when it comes to watercress, the microgreens are a marvel to behold. Why? Because they pack a nutritional punch that’s hard to beat.
Nutritional differences
You might wonder how such tiny leaves can be so potent. Well, let me tell you – these microgreens are bursting with vitamins. They’ve got higher levels of ascorbic acid and β-carotene than their mature counterparts. But that’s not all. These little powerhouses are also rich in antioxidants.
Phytochemical profile variations
Now, here’s where it gets fascinating. The phytochemical profile of watercress microgreens is unique. You see, they have higher levels of ascorbic acid and carotenoids. On the other hand, mature watercress offers more polyphenols and anthocyanins. It’s nature’s way of showing off its diversity.
Advantages of microgreens
So, what does this all mean for you? Well, imagine having a concentrated source of nutrients right at your fingertips. That’s what watercress microgreens offer. They’re not just nutritious – they’re also packed with flavor. And isn’t that what we all want in our food?
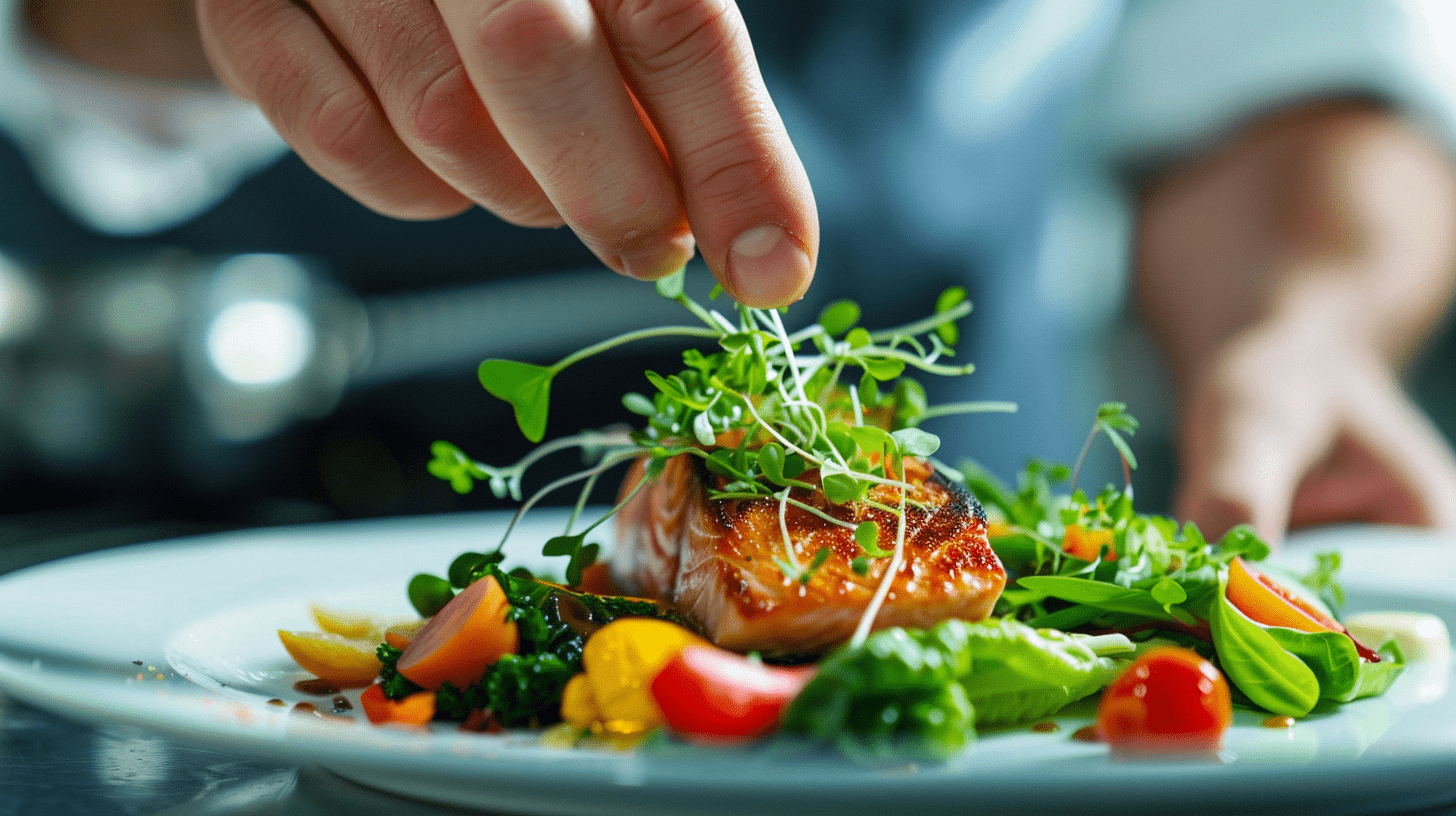

You’ll find watercress microgreens add a peppery zest to your dishes, reminiscent of mustard and radish.
Incorporate them into salads, sandwiches, and soups for a burst of freshness and nutrition.
Pair them with citrus fruits, creamy cheeses, or smoky meats to enhance your culinary creations with vibrant, contrasting flavors.
Flavor profile
The peppery, slightly tangy flavor of watercress microgreens can heighten a dish, offering both a burst of fresh taste and a wealth of nutrients.
Imagine: – The delight in a guest’s eyes as they savor the zest. – The joy of knowing you’re providing something nutritious and vibrant. – The satisfaction of crafting a meal that’s as healthy as it’s flavorful.
With each bite, you’re serving more than just food.
Incorporation into dishes
Elevate your culinary creations by seamlessly blending watercress microgreens into a variety of dishes. Their peppery zest and nutrient-rich profile can transform the ordinary into the extraordinary.
Imagine scattering these vibrant greens over a creamy soup or folding them into a fresh salad. Their crisp texture and vivid flavors will delight the senses, making every bite a nourishing act of love.
Pairing suggestions
When pairing watercress microgreens with other ingredients, consider their peppery bite and vibrant green hue to complement a range of flavors, from the creaminess of avocado toast to the tangy zest of citrus-infused seafood.
- Sprinkle atop creamy soups for a burst of freshness.
- Mix into salads for a nutritious crunch.
- Garnish grilled meats to enhance your dish.
Your guests will relish the thoughtful touch.
Seared Salmon with Rainbow Vegetable Medley and Watercress Microgreens
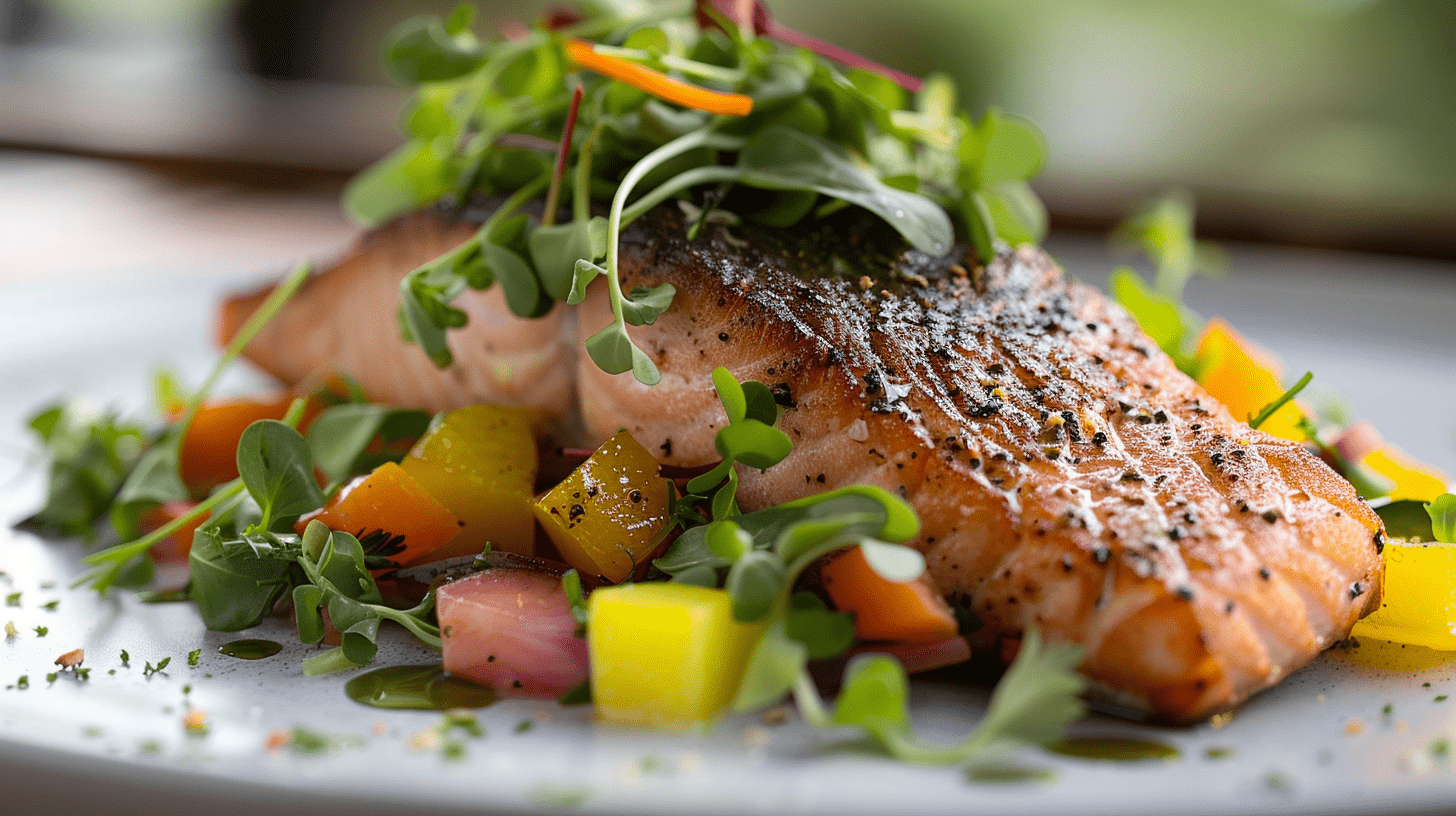
- Serving size: 8 oz
- Prep time: 20 minutes
- Cook time: 15 minutes
- Total time: 35 minutes
- Category: Main Course
- Method: Pan-searing, Roasting
- Cuisine: Modern American
- Yield: 4 servings
Ingredients:
- 4 (6 oz) salmon fillets
- 1 small zucchini, sliced
- 1 small yellow squash, sliced
- 1 red bell pepper, sliced
- 1 cup cherry tomatoes, halved
- 1 small red onion, thinly sliced
- 2 tbsp olive oil, divided
- Salt and freshly ground black pepper to taste
- 1 tsp dried herbs (thyme, rosemary, or herbs de Provence)
- 2 tbsp unsalted butter
- 1 lemon, juiced
- 1 cup watercress microgreens
Instructions:
- Preheat oven to 400°F (200°C).
- Toss zucchini, yellow squash, bell pepper, cherry tomatoes, and red onion with 1 tbsp olive oil, salt, pepper, and dried herbs. Spread on a baking sheet and roast for 15 minutes, stirring halfway through.
- While vegetables are roasting, pat salmon fillets dry with paper towels and season with salt and pepper.
- Heat the remaining 1 tbsp olive oil in a large skillet over medium-high heat. Once hot, add salmon fillets skin-side down and cook for 4-5 minutes until skin is crispy.
- Flip the salmon and add butter to the pan. Cook for another 2-3 minutes, basting with the melted butter, until the salmon is cooked through but still slightly pink in the center.
- Remove the salmon from the pan and squeeze lemon juice over the fillets.
- To plate, divide roasted vegetables among four plates. Place a salmon fillet on top of each vegetable portion.
- Garnish generously with watercress microgreens.
Serve immediately and enjoy your gourmet, nutritious meal!
The watercress microgreens add a vibrant pop of color and a fresh, peppery flavor that complements the rich salmon and roasted vegetables. Their delicate texture and nutrient-dense profile also elevate the dish’s visual appeal and nutritional value, making it a more well-rounded and sophisticated culinary experience.
Imagine transforming your skincare routine with the essence of watercress microgreens, a natural marvel celebrated for its anti-aging and anti-acne properties.
Often praised for its exceptional adaptability, watercress microgreens have found a niche in the cosmetics industry, where their potent bioactive compounds are utilized for skin health and rejuvenation.
You’ll find them in:
- Anti-aging serums that smoothen fine lines
- Skin-lightening creams enhance your natural glow
- Anti-acne treatments soothing troubled skin
Imagine your delight as you experience nature’s gentle touch.

When you begin growing watercress microgreens, start by ensuring the best conditions—think of a mix of light and warmth that mirrors spring’s gentle hug.
You’ll find that a blend of 50% green, 35% red, and 15% blue light fosters both lush growth and potent nutrition.
Harvesting around days 17-20, you’ll witness a vibrant tapestry of greens ready to enrich your meals.
Optimal growing conditions
Cultivating watercress microgreens requires precise control over light conditions. A blend of 50% green, 35% red, and 15% blue light is ideal for enhancing biomass growth and glucosinolate production.
You’ll witness:
- The joy of nurturing tiny green wonders
- The thrill of watching them flourish
- The satisfaction of contributing to others’ health
Your care transforms these microgreens into nutritional powerhouses.
Light requirements
To achieve optimal growth and maximize the nutritional value of your watercress microgreens, you’ll need to use a precise blend of 50% green, 35% red, and 15% blue light.
Think of it like painting a masterpiece; each hue plays an essential role.
From my own experience, this light recipe brings out the vibrant, lush greens that make your microgreens not just food but nourishment for the soul.
Harvesting time
Timing the harvest of your watercress microgreens at around 17-20 days guarantees you capture their peak nutritional potency and vibrant flavor. This precise timing secures:
- Peak nutrient content: Vitamins and minerals at their richest.
- Improved flavor: A burst of fresh, peppery taste.
- Visual pleasure: Lush, emerald-green leaves.
Imagine the joy of serving these nutrient-packed greens to those you care about.
Imagine growing watercress microgreens in your kitchen. Sounds simple, right? But there’s more to it than meets the eye. These tiny leaves pack a powerful nutritional punch. How can we make them even better?
Optimization of cultivation techniques
Future research holds the key. By optimizing cultivation techniques, we could unlock their full potential. But that’s not all. Light conditions play a crucial role, too.
Enhancement of bioactive compounds
What if we could elevate their nutritional profile even further? Clinical studies are on the horizon, ready to unveil profound health benefits. Can you picture watercress becoming a wellness staple?
Clinical studies on health benefits
The secret lies in balancing light spectra, adjusting nutrients, and perfecting harvest timing. But here’s the exciting part: specialized techniques could boost bioactive compounds dramatically.
Imagine the possibilities. Reduced cancer risk? Enhanced antioxidants? Improved anti-inflammatory responses? The future of health might just be growing in your kitchen.

How Do Watercress Microgreens Differ From Other Microgreens Nutritionally?
You’ll find watercress microgreens unique due to their high sodium content and exceptional antioxidant activity. They blend vibrant flavors with potent nutrients, making them a delightful, healthful garnish that stands out among other microgreens.
Can Watercress Microgreens Help With Weight Management?
You can harness watercress microgreens to aid weight management. Their low-calorie, nutrient-dense profile keeps you nourished without excess calories. Their rich fiber content also helps you feel full, making mindful eating a breeze.
Are There Any Potential Allergies Associated With Consuming Watercress Microgreens?
Yes, you might encounter allergies to watercress microgreens. Although rare, some people can experience reactions. Always listen to your body—your journey in serving others begins with ensuring your own health and well-being.
What Are the Best Storage Methods for Watercress Microgreens?
You should store watercress microgreens in a breathable container in the fridge. Make sure they’re dry and wrapped in a damp paper towel. This method preserves their vibrant essence, allowing you to serve freshness with every dish.
How Does Light Exposure Affect the Nutrient Content of Watercress Microgreens?
You’ll find that light exposure profoundly influences watercress microgreens’ nutrient content. Adopt a balanced light mix to optimize their essentials, as it nurtures their core, allowing you to serve nutrient-rich greens with love and dedication.
Watercress microgreens are tiny titans of nutrition, packing a punch that belies their delicate appearance.
But why should you care?
Because these vibrant greens offer a symphony of health benefits in every bite.
Recap of nutritional value
Picture a leaf bursting with vitamins A, C, and K. Now imagine it bristling with antioxidants and minerals. That’s watercress for you – a miniature marvel of nature’s design.
Potential impact on health and nutrition
But here’s the real magic: these microgreens don’t just nourish; they transform. They fight inflammation, support heart health, and infuse your body with vitality. Isn’t it amazing how something so small can make such a big difference?
So why not invite these little green wonders into your kitchen? Sprinkle them on your salads, tuck them into sandwiches, or blend them into smoothies. Your taste buds will be delighted, and your body will thank you.
After all, isn’t good health the greatest gift we can give ourselves?
INTERESTED IN MICROGREENS?
Join the community
Join more than 100,000 other health-conscious individuals and couples who visit our site and receive weekly emails from us to help them grow more microgreens to live healthier and longer lives.
References
- FoodData Central. (n.d.-c) https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-details/170068/nutrients.
- Lottenberg AM, Fan PL, Buonacorso V. Effects of dietary fiber intake on inflammation in chronic diseases. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2010 Jun;8(2):254-8. English, Portuguese. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1679-45082010MD1310. PMID: 26760015.
- Suzuki M, Ramezanpour M, Cooksley C, Lee TJ, Jeong B, Kao S, Suzuki T, Psaltis AJ, Nakamaru Y, Homma A, Wormald PJ, Vreugde S. Zinc-depletion associates with tissue eosinophilia and collagen depletion in chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology. 2020 Oct 1;58(5):451-459. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhin19.383. PMID: 32542237.
- Wald DS, Bishop L, Wald NJ, Law M, Hennessy E, Weir D, McPartlin J, Scott J. Randomized trial of folic acid supplementation and serum homocysteine levels. Arch Intern Med. 2001 12 March;161(5):695-700. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.161.5.695. PMID: 11231701.
- Vitamin A. Vision and Immune} Krinsky, N. I., & Johnson, E. J. (2005). Carotenoid actions and their relation to health and disease. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 26(6), 459–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2005.10.001
- Willcox JK, Ash SL, Catignani GL. Antioxidants and prevention of chronic disease. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2004;44(4):275-95. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690490468489. PMID: 15462130.
- T. H. Verhoeven, H. Verhagen, R. A. Goldbohm, P. A. van den Brandt, and G. van Poppel, “A review of mechanisms underlying anticarcinogenicity by brassica vegetables,” Chemico-Biological Interactions, vol. 103, no. 2, pp. 79–129, 1997.
- Belay Dereje, Jean-Christophe Jacquier, Elliott-Kingston, C., Harty, M., & Niamh Harbourne. (2023). Brassicaceae Microgreens: Phytochemical Compositions, Influences of Growing Practices, Postharvest Technology, Health, and Food Applications. ACS Food Science & Technology, 3(6), 981–998. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsfoodscitech.3c00040
- Widjaja, Taruna, et al. “Effect of Different Photoperiod Regimes in Combination with Natural and Artificial Light on Nutrient Uptake in Bok Choy (Brassica Rapa L.) Using an Internet of Things-Based Hydroponics System.” Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 8 May 2024, https://doi.org/10.4081/jae.2024.1579.
- Gao, M., He, R., Shi, R., Li, Y., Song, S., Zhang, Y., Su, W., & Liu, H. (2021). Combination of Selenium and UVA Radiation Affects Growth and Phytochemicals of Broccoli Microgreens. Molecules, 26(15), 4646. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154646
- Bhaswant, M., Shanmugam, D. K., Miyazawa, T., Abe, C., & Miyazawa, T. (2023). Microgreens: A Comprehensive Review of Bioactive Molecules and Health Benefits. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 28(2), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020867
- Mansi Gattani and Vasantha Kumari, Comprehensive evaluation of nutrient and phytochemical profile of bok choy (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis) at different growth stages. Sustainability, Agri, Food and Environmental Research, (ISSN: 0719-3726), 11(X), 2023






















